We have successfully completed a digital project aimed at improving the collection of land tax payments in the city of Izhevsk.
In this project, we utilized technologies such as Smart Cadastre, Big data, and AI to analyze the current state of land use.
As a result, we identified problems causing deficiencies in payment collection, such as insufficiencies of data, data collisions and violations of building codes.
Project stages
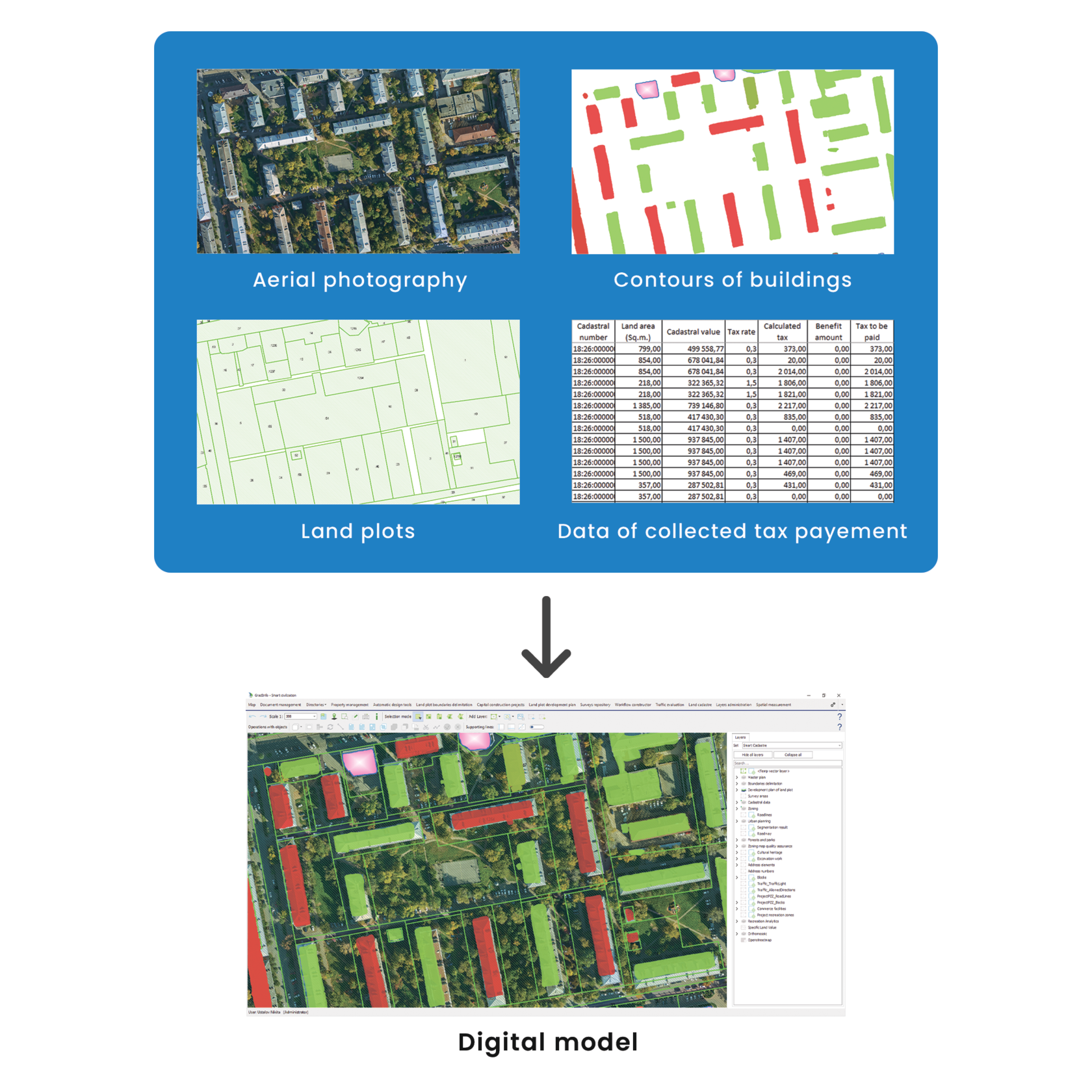
1) Collection of raw data from various sources.
● Creation of digital map for analysis of actual build-up area. We conducted aerial photography and obtained two types of spatial data: a high-precision orthophotomap for visual analysis and a colored point cloud for detecting buildings using artificial intelligence.
In this project, we utilized technologies such as Smart Cadastre, Big data, and AI to analyze the current state of land use.
As a result, we identified problems causing deficiencies in payment collection, such as insufficiencies of data, data collisions and violations of building codes.
Project stages
1) Collection of raw data from various sources.
● Creation of digital map for analysis of actual build-up area. We conducted aerial photography and obtained two types of spatial data: a high-precision orthophotomap for visual analysis and a colored point cloud for detecting buildings using artificial intelligence.
● Collection of data on land plots and buildings from government and municipal information systems, including paper documents. Such data includes plot boundaries, plot area, permitted land use type, cadastral value, tenure rights, etc.
● Acquisition of data of tax charges and payments from the tax authority databases, as well as from the of the lease administrator database.
2) Converting raw data to the digital model format.
All data was uploaded into a data lake, and then converted into an integrated digital platform using specially designed converters. The conversion included linking data from different database sources.
We performed a feature recognition AI technic to obtain relevant data about building location from aerial photography.
Thus, we collected big data for further automated data processing, using artificial intelligence.
We performed a feature recognition AI technic to obtain relevant data about building location from aerial photography.
Thus, we collected big data for further automated data processing, using artificial intelligence.
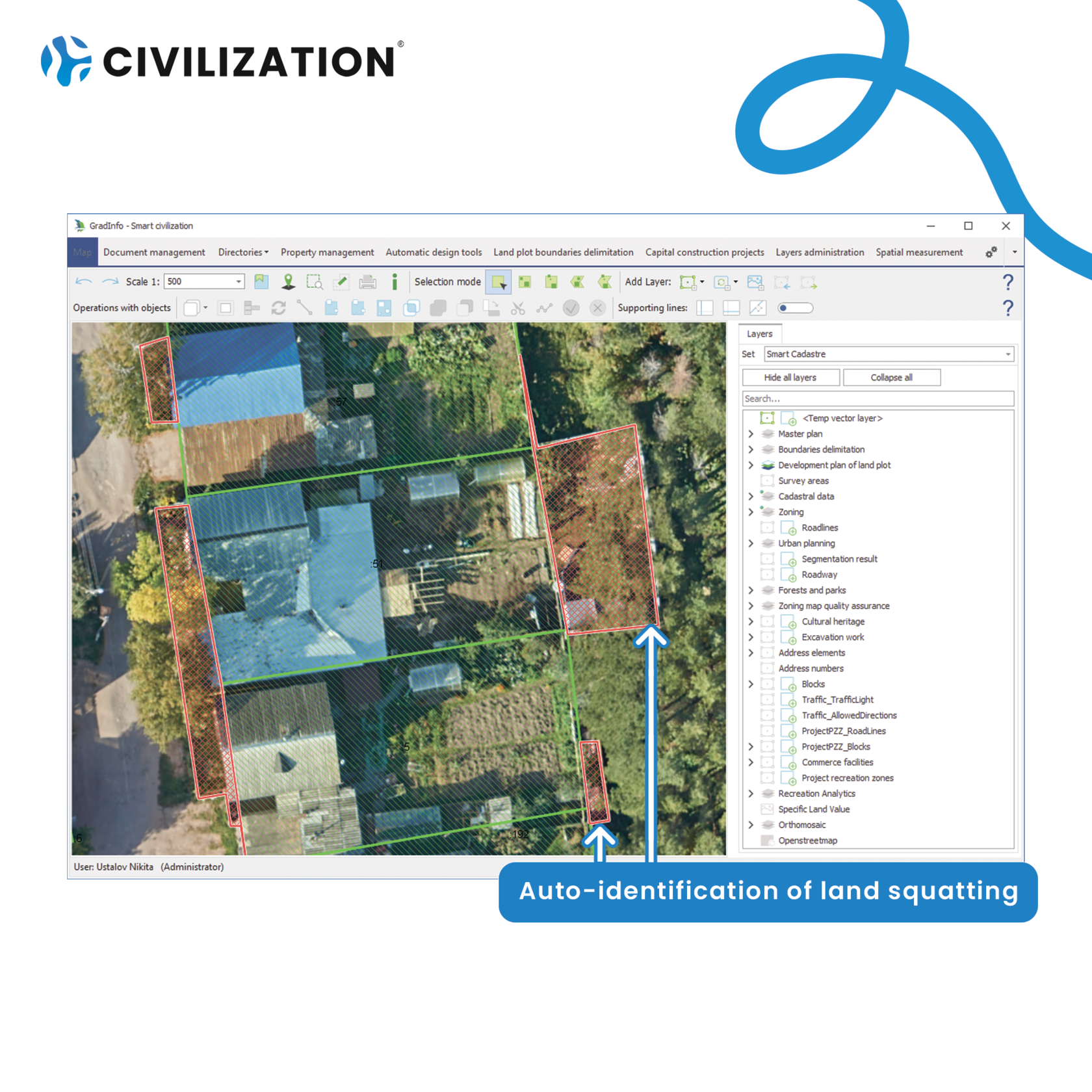
3) Auto-identification of problems and irregularities of data
By means of Auto-identification of problems and irregularities in data we have identified a number of problems that result in a lower tax collection. Some examples of identifications are listed below:
● Land squatting. Use of land beyond the boundaries of the land plots, unregistered buildings/construction on the land:
By means of Auto-identification of problems and irregularities in data we have identified a number of problems that result in a lower tax collection. Some examples of identifications are listed below:
● Land squatting. Use of land beyond the boundaries of the land plots, unregistered buildings/construction on the land:
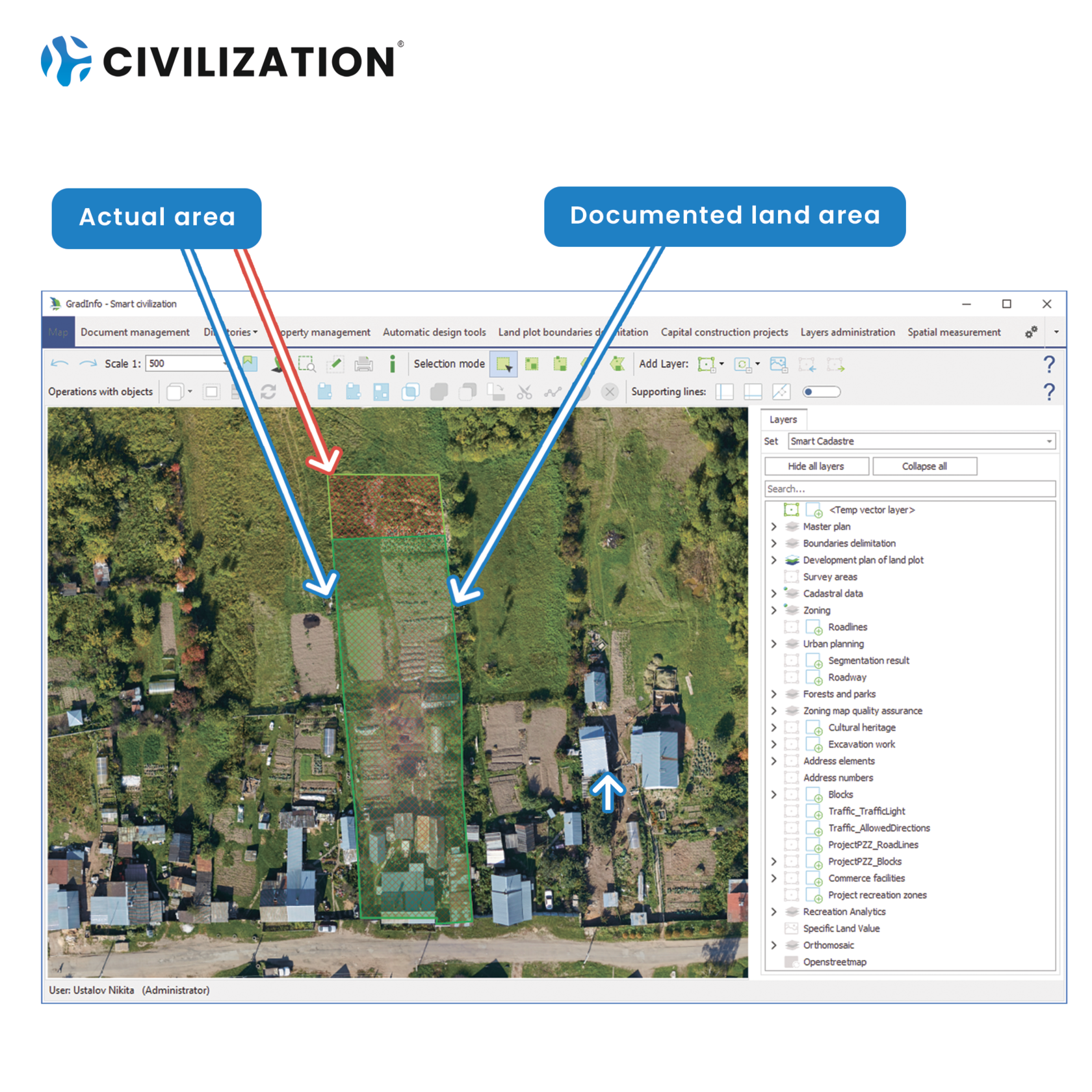
● Land plots, the documented area of which differs from the actual area:
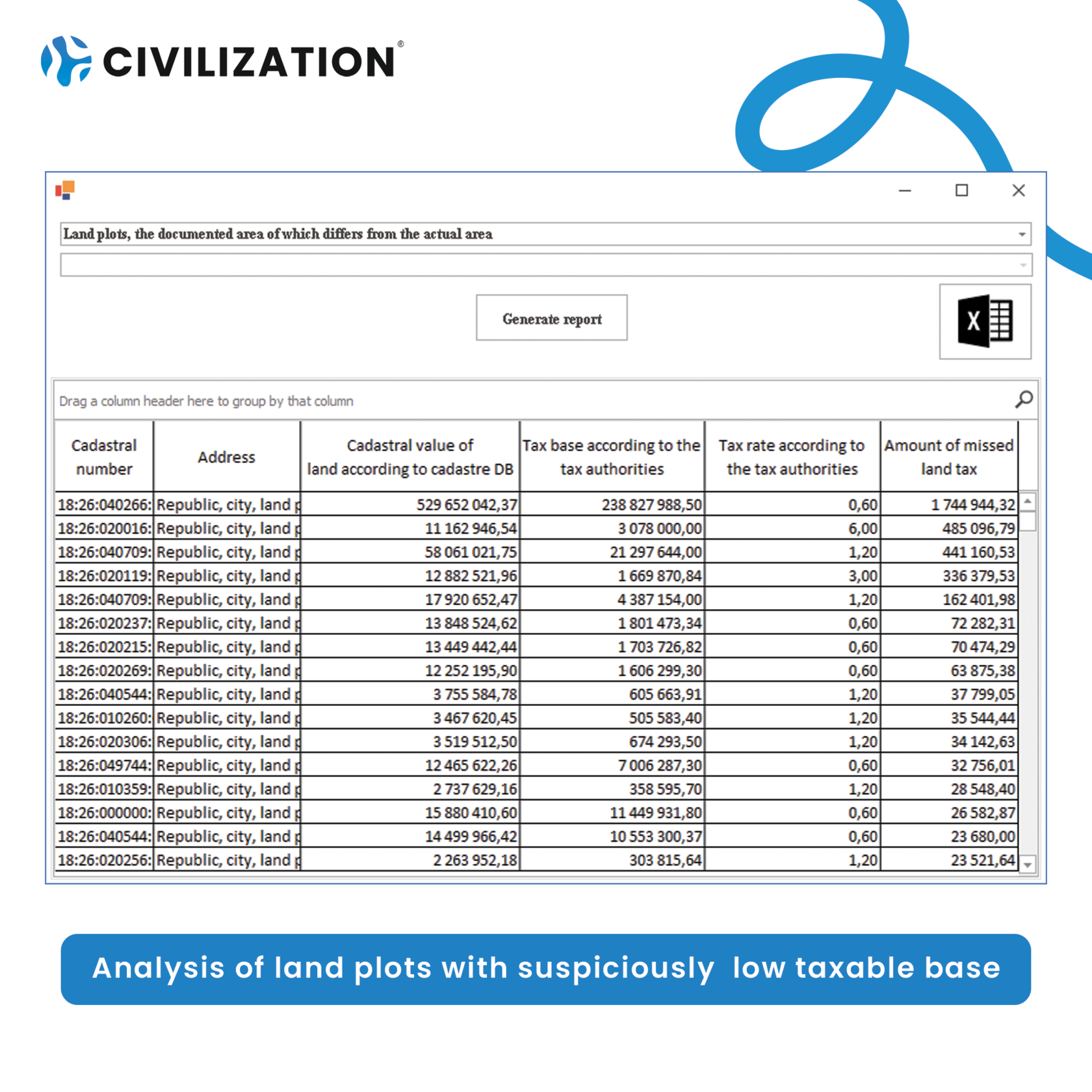
● Land plots with a suspiciously low taxable base:
The outcome
During the analysis, it was found that 3% of the land sites have problems that do not allow to effectively collect tax on them. 4% of the area is used outside the boundaries of land.
In the first year after the beginning of analysis we managed to boost the collection rate by 4 times project cost. During the next year it is planned to increase the collection rate by the same amount.
In the first year after the beginning of analysis we managed to boost the collection rate by 4 times project cost. During the next year it is planned to increase the collection rate by the same amount.
